[最も共有された! √] 2/11 decimal expansion 222907-2/11 decimal expansion
Introduction to method We avoid the decimal point until write at the end 11 is more that 2 but we can and may write 2 as × 1 10 where the 1 10 is an adjustment The is more that 11 so the division is a bit more strait forward We reintroduce the decimal at the very end by multiplying the answer by EXERY adjuster of 1 10Decimal expansion is the form of a number that has a decimal point, either actual or implied Examples of numbers with actual decimal points are 102 and (2/11 =A 2/7 B12 C5/8 D2/11

Activating Prior Knowledge Module Page Ppt Download
2/11 decimal expansion
2/11 decimal expansion-The principal square root of most numbers is an irrational number with an infinite decimal expansion As a result, the decimal expansion of any such square root can only be computed to some finiteprecision approximation However, even if we are taking the square root of a perfect square integer, so that the result does have an exact finite Click here 👆 to get an answer to your question ️ write 2\11 in decimal form and what kind of decimal expansion manohar007 manohar007 Math Secondary School answered Write 2\11 in decimal form and what kind of decimal expansion 2 See answers MiSSiLLuSioN MiSSiLLuSioN 2/11 in the form of decimal is or 018 (bar on




Ex 1 3 1 Write The Following In Decimal Form And Say Ex 1 3
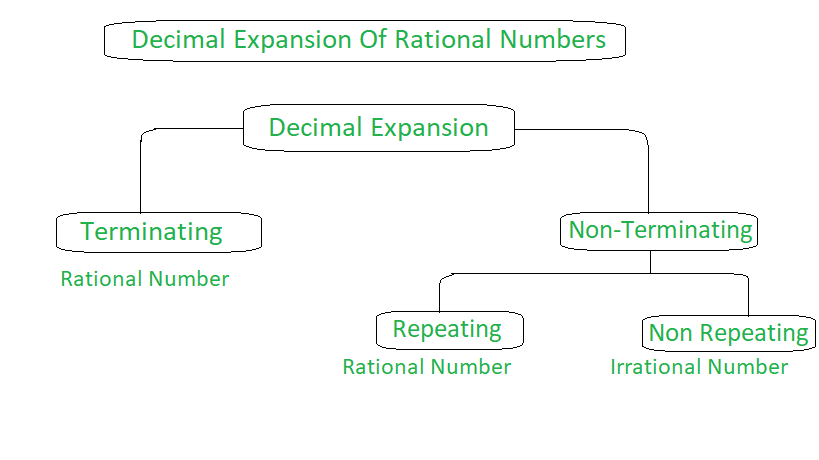
Best answer We can observe that while dividing 2 by 11, first we got the remainder as 2 and then 9, which will continue to be 2 and 9 alternately Therefore, we conclude that 2/11 = or 2/11 = 018, which is a nonterminating decimal and recurring decimal ← Prev Question Next Question →To write 4/11 as a decimal you have to divide numerator by the denominator of the fraction We divide now 4 by 11 what we write down as 4/11 and we get And finally we have 4/11 as a decimal equalsAny number, rational or irrational, has a decimal expansion Sometimes it goes on forever For example, the rational number \(\frac{2}{11}\) has the decimal expansion \( \) with the 18s repeating forever Every rational number has a decimal expansion that either stops at some point or ends up in a repeating pattern like \(\frac2
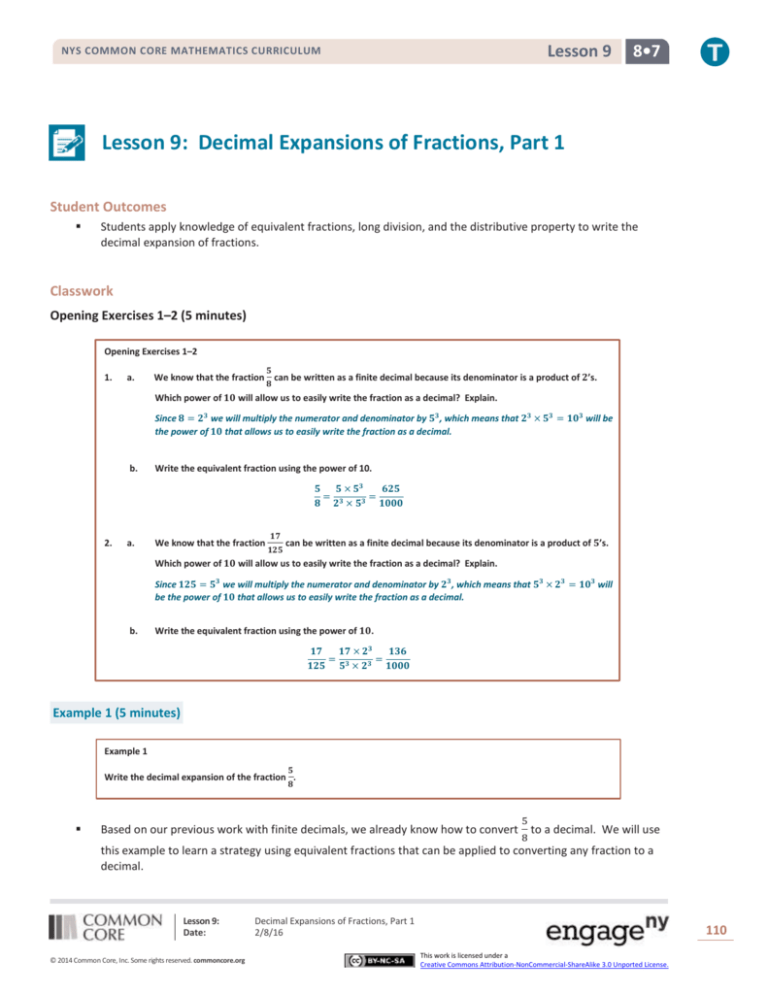
How to convert fraction to decimal Method #1 Expand the denominator to be a power of 10 Example #1 3/5 is expanded to 6/10 by multiplying the numerator by 2 and denominator by 2Confucius Show me Another Quote! Eureka Math Grade 8 Module 7 Lesson 8 Example Answer Key Example 1 Show that the decimal expansion of is 65 Use the example with students so they have a model to complete Exercises 1–5 → Show that the decimal expansion of is 65 Students might use the long division algorithm, or they might simply observe = = 65
98% (43 ratings) for this solution Step 1 of 5 We have to convert the binary expansion of the given integers to a decimal expansion a) The Decimal expansion is Chapter 42, Problem 4E isIn the last activity students explore the decimal expansion of \(\frac{2}{11}\) They use long division with repeated reasoning (MP8) to find that \(\frac{2}{11}=\dots\) Students realize that they could easily keep zooming in on \(\frac{2}{11}\) because of the pattern of alternating between the intervals \Sometimes you get the maximum number of digits and sometimes you don't when the denominator is 7 you get the maximum number of digits (71=6)



Decimal Expansion Of Real Numbers Geeksforgeeks




Ssc Mathematics Chapter 1 Real Numbers
2 11 = 3 2 11 The goal is to use rational approximation to determine the decimal expansion of a number, instead of having to check a series of intervals as we did with the decimal expansions of irrational numbers To determine the decimal expansion of 35 11, focus only on the fraction 2 11 Then, methodically determine between which intervalNCERT Solutions for Class 9 Math Exercise 13 Question 1 Write the following in decimal form and say what kind of decimal expansion each has i)While working with binary may initially seem confusing, understanding that each binary place value represents 2 n, just as each decimal place represents 10 n, should help clarifyTake the number 8 for example In the decimal number system, 8 is positioned in the first decimal place left of the decimal point, signifying the 10 0 place Essentially this means




2 11 10 In Decimal Form What Is 2 11 10 As A Decimal



Silo Tips Download Activity 2 1 Extending The Place Value System
The decimal expansion for e π π e is given by A e π − π e = {\displaystyle e^{\pi }\pi ^{e}=} 0681 534 914 418 223 532 301 934 163 404 812 352 676 791 108 603 519 744 242 043 855 457 416 310 291 334 871 198 452 244 340 406 11 Hence, decimal expansion is nonterminating recurring 3/13 = (v) 2/11 Solution In the given question, we get Here, the remainder never becomes zero and remainders repeat after a certain stage Hence, decimal expansion is nonterminating recurring 2/11 = (vi) 329/400 Solution In the given question, we getMore indicators can be found in the "FACTFILE" section on the homepage for each state



Write The Following In Decimal Form And Say What Kind Of Decimal Expansion Each Has 2 11 Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community



2
We can see that while dividing 2 by 11, first the remainder is 2 then 9, which will continue to be 2 and 9 alternately Therefore, 2/11 = or 2/11 = 018 which is a nonterminating and recurring decimalClass 9 Maths Number Systems Real numbers in Decimal form Real numbers (both rational & irrational) can be represented in decimal form Eg 10/3, 7/8, √2 can be represented in decimal form There are 3 different cases for rational number conversion to decimal form Rational Number Case 1 The remainder becomes 02 4/11 is equal to in decimal form Use our fraction to decimal calculator to convert any fraction to a decimal and to know if it is a terminating or a recurring (repeating) decimal



Decimal Representation Of Rational Numbers




Notes On Real Numbers
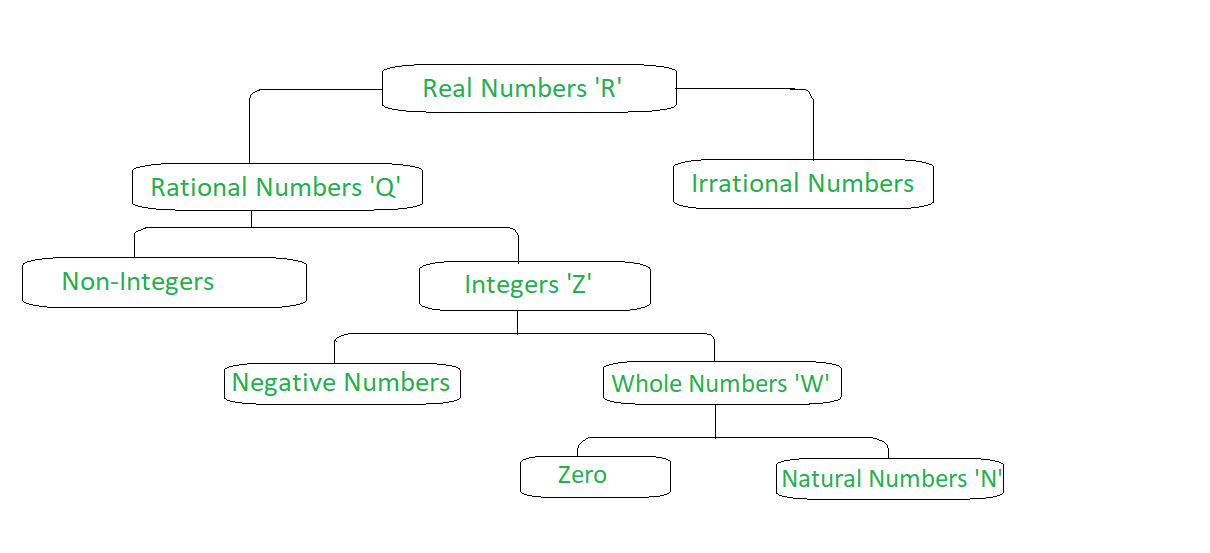
Thus, we say them as irrational numbers IRRATIONAL NUMBERS 1)The numbers which cannot be written in p/Q form and known as irrational numbers 2) the decimals which are non terminating and non recurring are known as irrational numbers 3) is the natural number "n" is not a square number, then the square root of the "n" is an irrational numberTo write 2/11 as a decimal you have to divide numerator by the denominator of the fraction We divide now 2 by 11 what we write down as 2/11 and we get And finally we have 2/11 as a decimal equals By Long Division, the number of digits in the repeating block of digits in the decimal expansion of = \(\frac{1}{17}\) = 16 ∴ The answer is verified Question 6




Express 2 11 In Decimal Form Hint If Quotient Repeats They Are Called Recurring Decimal




Fraction To Decimal 11 25 Video Khan Academy
Decimal Expansion The decimal expansion of a number is its representation in base 10 For example, the decimal expansion of is 625, of is , and of is where (mod 2, 5) Therefore, the numbers with finite decimal expansions are fractions of this form The number of decimals is given by Example 6 Express \(\frac { 2 }{ 11 }\) as a decimal fraction These expansion are not finished but digits are continusely repeated so we use a line on those digits, called bar \((\bar{a})\) So we can say that rational numbers are of the form either terminating, non repeating or non terminating repeating (recurring) how to find the decimal expansion of 2 upon 11 and stating the type of decimal expansion In this video we will learn how to divide 2 by 11 and covert it int
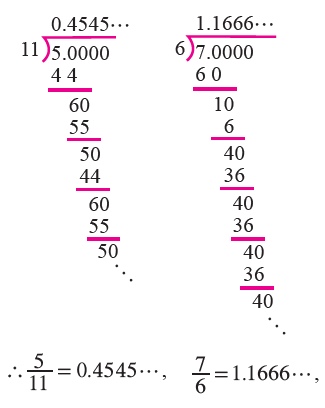



Decimal Representation Of Rational Numbers




Egyptian Fraction Wikipedia
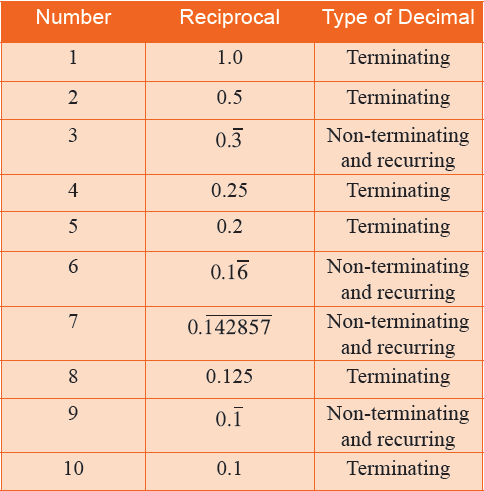
Example Find the decimal expansion of 3/6 Here, the quotient is 05 and the remainder is 0 Rational number 3/6 results in a terminating decimal Case 2 Remainder not equal to zero Example Express 5/13 in decimal form Here, the quotient is and the remainder is not zero Notice that the number384 after the decimal is repeating 2/11 has a terminating decimal of A repeating decimal expansion can be represented by placing a bar over the repeating sequence of digits So in our example 2/11 = = 0bar(18) Algebra




How To Express In Decimal Form



3
Decimal expansion of the rational number 11 / 2 raise to 3 into 5 raise to 2 will terminate after how many places of decimal Answers 1 Get Other questions on the subject Math Math, 10, jdavis2310 Four years ago, my fathers age was 4 times that of my age at present the sum of my father age and that of mine is 53 years, whatStep 2 Write it as a decimal 11/2 = 55 55 is the decimal representation for 11/2 For Percentage Conversion step 1 To represent 55 in percentage, write 55 as a fraction Fraction = 55/1 step 2 multiply 100 to both numerator & denominator (55 x 100)/ (1 x 100) = 550/100 550% is the percentage representation for 11/2The average life expectancies of males for several states are shown in the table Express each decimal in the form q p and arrange the states from the least to the greatest male life expectancy Statewise data are included below;




2 11 To Decimal Expansion




Write The Following Decimal Form And Say What Kinds Of Decimal Expansion Each Has 1 36 100 2 3 13 Brainly In
Example 5 Chapter 1 Class 9 Number Systems NCERT Solution Find the decimal expansions of 10/3, 7/8 and 1/7 To find the Decimal expansions, we divide the numbers Dividing 10 by 3, we get 10/3 = In the example of 7/8 , we found that the remainder becomes zero after some steps and the decimal expansion of 7/8 = 0875 Other examples are ½ = 05, 639/250 = 2556 In all these cases, the decimal expansion terminates or ends after a finite number of steps We call the decimal expansion of such numbers as terminatingConvert Decimal n to base b Expansion 1Divide n by b 2The remainder is the rightmost digit in base b expansion of n 3The quotient becomes the new dividend 4Stop if quotient is zero 5Repeat 42 pg 255 # 3 Convert the binary expansion of each of these integers to a decimal expansion a)(1 1111) 2 1 42 11 023 1122 1121 112 =



Example Output Formatting Mth 337



1
Which number has a terminating decimal expansion? Ex 13 Q1 v 9th maths Number System Decimal expansion of 2/11 3/7= again, always divide the denominator into the numerator and divide until you clearly see what repeats the repetend cannot exceed 1 less than the denominator;




Real Numbers




What Is 11 15 As A Decimal
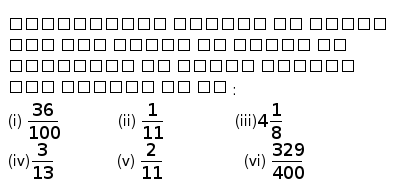
Types of Rational Decimal Expansion 2 I Proof m=n is terminating if and only if m=n = m 2u5v Mt 10t I m=n is simpleperiodic if and only if we can cancel the decimals by shifting one period, ie (10r n1)m= = MsI m=n is delayedperiodic if and only if we can cancel the decimals by shifting one period and moving the period t places, ie Transcript Ex 13, 1 Write the following in decimal form and say what kind of decimal expansion each has (i) 36/100 36/100 = 036 , Terminating expansion Ex13, 1 Write the following in decimal form and say what kind of decimal expansion each has (ii) 1/11 ∴ 1/11 = = 0(09) ̅ Non – terminating and repeatingEmail This Page To A Friend To convert this fraction to a decimal, just divide the numerator (1) by the denominator (11) So, 1 / 11 = 1 ÷ 11 = Approximated Values 1 / 11 = 009 rounded to 1 significant figure 1 / 11 = 0091 rounded to 2 significant figures




The Decimal Representation Of 11 2 3 5 Will A Terminate After




Write The Following In Decimal Form And Say What Kind Of Decimal Expansion Each Has I 36 Youtube
There are 16 digits in the repeating block of the decimal expansion of 1/17 6 Look at several examples of rational numbers in the form p/q (q ≠ 0), where p and q are integers with no common factors other than 1 and having terminating decimal representations (expansions)So, 167 has a terminating decimal expansion (ii) 150=2×3×52 =2×3×5213 Since it is not in the form 2m×5np, has a nonterminating and recurring decimal expansion Decimal Expansion Before going into a representation of the decimal expansion of rational numbers, let us understand what rational numbers are A Rational Number is a number that can be written in form of p/q where p, q are Integers and q != 0 Example 2/3, 1/4, 4/5, etc Rational numbers are denoted by Q As every Integer can be represented



Write The Following In Decimal Form And Say What Kind Of Decimal Expansion Each Has Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community




Question 1 Write The Following In Decimal Form And Say What Kin
In a comment on a previous post about rational numbers and decimal expansions, Steve Gilberg noted I've been fascinated at how any multiple of 1/7 that's not an integer repeats the same digits in decimal expression, only starting at different points in the sequence 1/7 = 3/7 = 2/7 = 6/7 =HOW TO CHECK WHICH TYPE OF DECIMAL EXPANSION If a rational number p/q, q ≠ 0 can be expressed in the form p/ (2m x 5n) , where p ∈ Z and m, n ∈ W, then rational number will have a terminating decimal expansion Otherwise, the rational number will have a non terminating and recurring decimal expansion Decimal Expansion The decimal expansion of a number is its representation in base10 (ie, in the decimal system) In this system, each "decimal place" consists of a digit 09 arranged such that each digit is multiplied by a power of 10, decreasing from left to right, and with a decimal place indicating the s place For example, the number with decimal expansion




Prime Factors Of The Denomina See How To Solve It At Qanda



Q Tbn And9gcsrrvd P3knp6qplrfmuwlgy3ydgf90thys 0i52 Ipgxdecz5a Usqp Cau
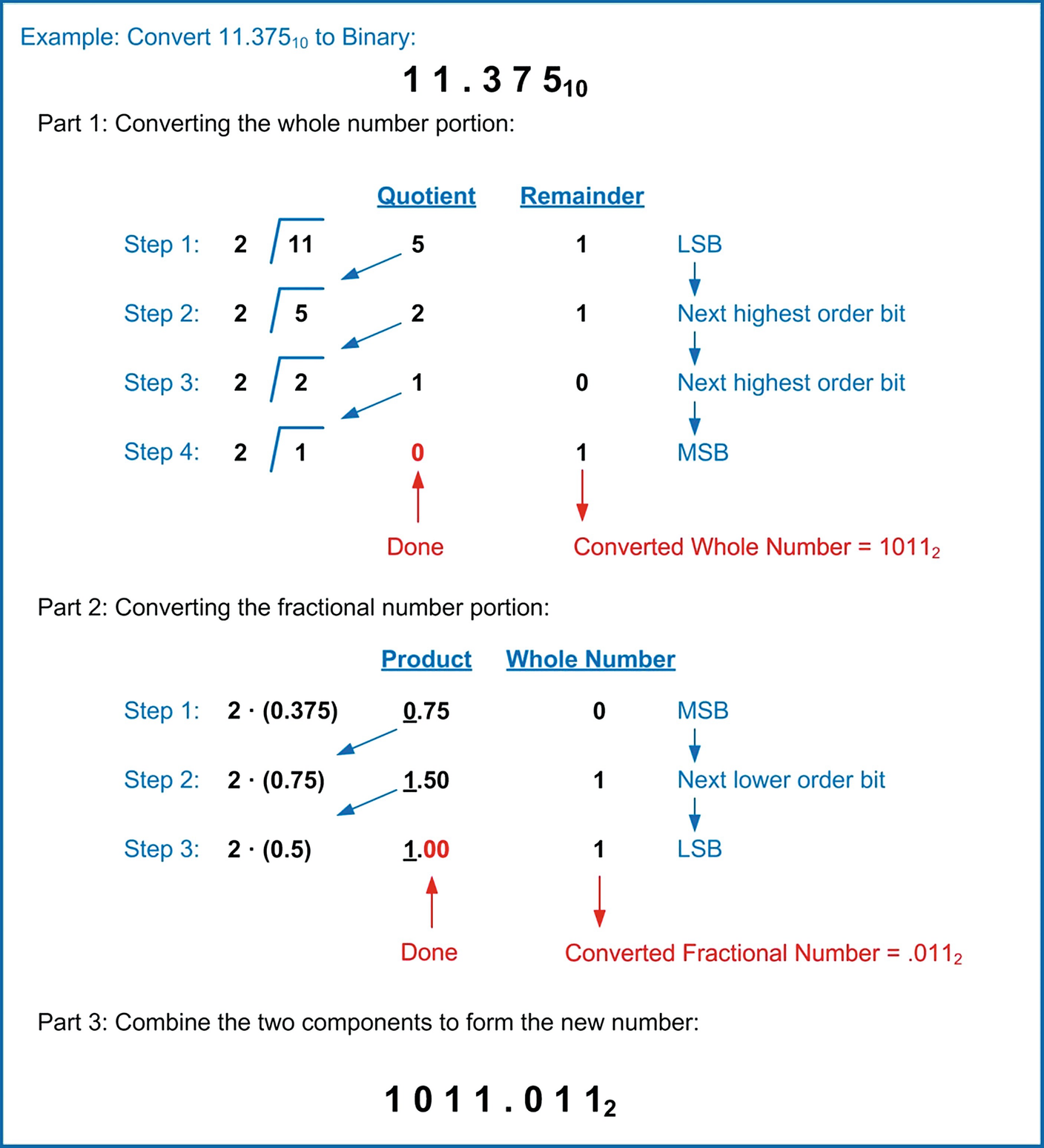
How to convert binary to decimal For binary number with n digits d n1 d 3 d 2 d 1 d 0 The decimal number is equal to the sum of binary digits (d n) times their power of 2 (2 n) decimal = d 0 ×2 0 d 1 ×2 1 d 2 ×2 2 Example Find the decimal value of 2The decimal expansion of a number is its representation in base 10 (ie, the decimal system) For example, the decimal expansion of 25 2 is 625, of pi is , and of is The decimal expansion of a number can be found in Mathematica using the command RealDigitsn, or equivalently, RealDigitsn, 10 The decimal expansion of a number may terminate (in which 2/11 in decimal form with out actual division and it is terminating or non terminating Get the answers you need, now!




Write The Following In Decimal Form And Say What Kind Of Decimal Expansion Each Has Cbse Class 9 Maths Learn Cbse Forum




How To Find The Decimal Expansion Of 2 Upon 11 And Stating The Type Of Decimal Expansion Youtube
From the decimals it is a recurring number, but it is nonterminating Therefore, it is a rational number (v) We see that the decimal expansion of this number is nonrepeating and nonrecurring Therefore, it is an irrational number Exercise 14 1 Visualize 3765 on the number line, using successive magnification Solution




Ex 1 3 1 Write The Following In Decimal Form And Say Ex 1 3




How To Express In Decimal Form




Cmsc 56 Lecture 10 Integer Representations Algorithms




What Is 2 11 In Decimal Form



What Is The Decimal Expansion Of 5 16 Quora



How Do You Write The Decimal Expansion For 6 11




Write The Following In Decimal Form And Say What Kind Of Decimal Expansion Each Has I 36 100 Ii 1 11 Number Systems Forum




Write In Decimal Form Of 2 11 And Also Find The Nature Of The Decimal Number Cbse Class 9 Maths Learn Cbse Forum
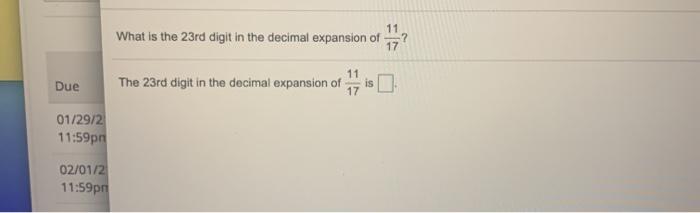



What Is The 23rd Digit In The Decimal Expansion Of 17 Chegg Com



Webmath Com Doing Math With Fractions




Exampie Us Exercise 1 3 1 Write The Following In Decimal F Scholr




Write Frac 2 11 In Decimal Form And Say What Kind Of Decimal Expansion Has Snapsolve




Rational Number Class 9 Notes




Question 1 Write The Following In Decimal Form And Say What Kin




Ex 1 3 1 Write The Following In Decimal Form And Say Ex 1 3




Write The Following In Decimal Form And Say What Kind Of Decimal
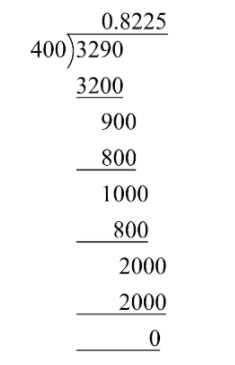



Write The Following In Decimal Form And Say What Kind Class 9 Maths Cbse




Easy Way To Find Decimal Expansion Of Rational Numbers Rational Numbers In Decimal Form Youtube




Activating Prior Knowledge Module Page Ppt Download



Hi Static Z Dn Net Files D6f F4c68a69c72f66e65f7bd00cd Pdf




Find The Decimal Form 1 11 And Write The Nature Of Its Decimal Expansion Brainly In



What Is 1 11 As A Decimal Quora



What Is The 23rd Digit In The Decimal Expansion Of 17 Chegg Com



Write The Following In Decimal Form And Say What Kind Of Decimal Expansion Each Has I 36 100 Ii 1 11 Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community




Math Numbers And Functions Homework 6 Solutions




Decimal Expansion Of Rational Number With Solved Examples




Math Numbers And Functions Homework 6 Solutions



What Is The Decimal Expansion Of 5 16 Quora




Ex 1 3 Q1 V 9th Maths Number System Decimal Expansion Of 2 11 Youtube



Converting Fractions To Decimals How To Convert Fraction Into Decimal




Write The Following In Decimal Form And Say What Kind Of Decimal Expansion Each Has I 36 100 Ii 1 11 Iii 41 5 Iv 3 13 V 2 11 Vi 329 400 Snapsolve




Number Systems Introduction Ppt Download




Write 2 11 In Decimal Form And It S Decimal Expansion I Cbse Class 9 Maths Youtube




Pdf Decimal Expansion Of 1 P And Subgroup Sums




1 Write The Following In Decimal Form And Say What Kind Of Decimal Expansione N Begin Array L L Text 1 Frac 36 100
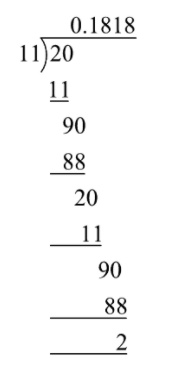



Write The Following In Decimal Form And Say What Kind Class 9 Maths Cbse




6 If 2 X 2 Cdot 3 2 X 6 36 Find The Value Of X 7 Write Frac 2 11 In The Decimal Form And Say What Kind Of Decimal Expansion It Is 8 Express 0 Overline 35 In The Frac P Form




Decimal Expansion Of Rational Numbers Video Lesson Transcript Study Com




The Decimal Representation Of Frac 11 2 Will A Terminate After 1 Decimal Place B Terminate After 2 Decimal Places C Terminate Atter 3 Decimal Places D Not Terminate



1



What Is The 23rd Digit In The Decimal Expansion Of 17 Chegg Com



Grade 8 Mathematics Module 7 Topic B Lesson 9



Decimal Expansion Of Real Numbers Geeksforgeeks




Ex 1 3 1 Write The Following In Decimal Form And Say Ex 1 3



2



Fractions And Decimals




Write Numbers In Decimal And Write Decimal Expansion Type I 36 100 Ii 1 11 Iii 4 1 8 Iv 3 13 V 2 11 Vi 329 400




Write In Decimal Form And Say What Kind Of Decimal Expansion It Is 2 11 329 400 Maths Number System Meritnation Com




Class 9 Mathematics Number System Exercise 1 3 Part 3 Solution




Binary Fractions And Fractional Binary Numbers




Ex 1 3 1 Write The Following In Decimal Form And Say Ex 1 3



Number Systems Springerlink




Ex 1 3 1 Write The Following In Decimal Form And Say Ex 1 3




Write The Following In Decimal Form And Say What Kind Class 9 Maths Cbse




Decimal Representation Of Rational Numbers Solved Examples



Illustrative Mathematics




Write Numbers In Decimal And Write Decimal Expansion Type I 36 100 Ii 1 11 Iii 4 1 8 Iv 3 13 V 2 11 Vi 329 400




Write The Following In Decimal Form And Say What Kind Of Decimal Expansion Each Has 15 100 1 9 Brainly In




Question 1 Write The Following In Decimal Form And Say What Kind Of Decimal Expansion Each Has Swiflearn




Write Each Of The Following In Decimal Form And Say What Kind Of
.png)



Number System Ncert Exercise 1 3 Part1 Decimal Expansions 9th Math




Write The 36 100 1 11 3 13 2 11 329 400 In Decimal Form And Say What Kind Of Decimal Expansion Youtube




The Decimal Representation Of 11 2 3 5 Will A Terminate After




The Decimal Representation Of Frac 11 2 Will A Terminate After 1 Decimal Place B Terminate After 2 Decimal Places C Terminate Atter 3 Decimal Places D Not Terminate




State Whether Rational Number 2 11 Is Terminating Or Non Terminating Recurring Brainly In




Question 1 Write The Following In Decimal Form And Say What Kind Of Decimal Expansion Each Has Swiflearn



Example Output Formatting




Number Decimals Wikisp Place Value And Order For Decimals Write A Terminating Decimal As A Common Fraction Add And Subtract Decimals Multiply And Divide A Decimal By A Power Of




Exercil In Decimal Form And Say What Kind Of Decimal Expansi Scholr




Decimal Expansion Of Rational Number With Solved Examples



Www Uio No Studier Emner Matnat Math Mat4010 V18 Forelesningsnotater Decimal Expansion Notes Pdf




Write 2 11 In Decimal Form And What Kind Of Decimal Expansion Brainly In




Real Numbers




Decimal Place Value Worksheets 4th Grade




Decimal Representation Of Rational Numbers Solved Examples




Rational Numbers Powerpoint Slides


コメント
コメントを投稿